总结卡片
SUMMARY
23
Changshou.com
淫羊藿苷
(Icariin)
淫羊藿苷(Icariin)是从传统中药淫羊藿中提取的一种黄酮类化合物(分子式: C₃₃H₄₀O₁₅),是淫羊藿的主要活性成分之一。在传统中医中,淫羊藿常用于补肾壮阳、强筋健骨。
什么是淫羊藿苷?
淫羊藿苷(Icariin, ICA)是一种天然黄酮类化合物单体,来源于淫羊藿干茎叶提取物[1]。淫羊藿属含有丰富的类黄酮和木脂素,其中类黄酮,尤其是淫羊藿苷,是最丰富也是重要的物质[1,2]。
淫羊藿苷目前在市场上主要应用在补肾壮阳和治疗骨关节炎两个方面上,但淫羊藿苷还对心血管疾病、月经失调、哮喘和免疫调节有作用,也用于治疗与年龄相关的疾病,如神经退行性变、认知丧失、抑郁症、慢性炎症、糖尿病和骨质疏松症等[1-5]。
ICA 不溶于水,必须从肠腔吸收才能被全身利用[6,7]。这导致 ICA 的药代动力学差、生物利用度低。有研究表明,将 ICA 制备成脂质体或胶束制剂,可以延长生物半衰期、改善药代动力学[8,9]。
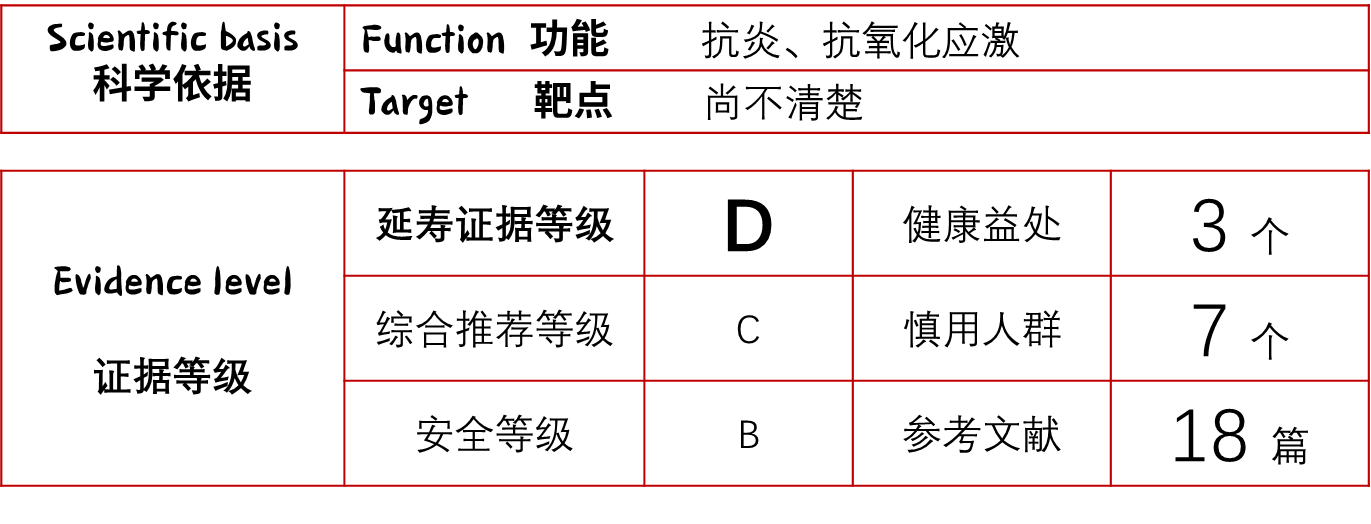
淫羊藿苷:延寿证据等级 D,为什么?
淫羊藿苷及其活性代谢物淫羊藿苷 II,可以将线虫的平均寿命延长 20.67% [10]。
根据长寿之家Changshou.com制定的《长寿成分评级标准(2025版)》,淫羊藿苷的延寿证据等级为 D。
补充淫羊藿苷有什么好处?
淫羊藿苷目前在动物实验中展现出了对糖尿病、心血管疾病、类风湿关节炎、骨质疏松症、神经系统疾病、甚至癌症的治疗能力[1-5,11],但目前在人体实验中验证过的临床益处较少,主要有以下几点:
治疗男性不育症:一项纳入 161 篇研究论文的荟萃分析结果显示,中药淫羊藿中的类黄酮(包括淫羊藿苷)对男性生殖功能障碍有益,包括少精症、无精症、勃起功能障碍等[12]。
治疗骨质疏松:一项为期 24 个月的随机双盲安慰剂对照临床试验,招募了 100 名健康绝经后晚期妇女,平均分配到实验组与对照组,实验组每天服用 60 毫克淫羊藿苷、15 毫克大豆苷和 3 毫克木黄酮,发现可以预防绝经后晚期妇女的骨质流失[13]。
一项汇集了 17 项随机对照试验的荟萃分析结果显示,含有淫羊藿的草药可以有效增加骨质疏松症患者的骨矿物质密度[14]。
一项随机双盲对照试验招募了 58 名绝经后妇女,每天服用 740 毫克的淫羊藿提取物(主要含有淫羊藿苷 II),持续 6 周,有利于骨合成代谢[15]。
改善慢阻肺:一项纳入 1975 名慢阻肺(COPD)患者的网状荟萃分析显示,淫羊藿(Yam-Epimedium)可以减少 COPD 患者的呼吸困难情况[16]。
淫羊藿苷的安全性与副作用
淫羊藿苷相对安全,但也会有一些不良反应,如长期服用可能引起口干、恶心、胃部不适、腹胀便秘等,少数人可能会出现心悸、头晕等不适症状。
淫羊藿苷是如何发挥功能的?
淫羊藿苷抗衰老作用的潜在机制仍在深入研究中,目前认为其可能通过多种途径发挥作用。其主要机制可能涉及调节衰老相关的信号通路,特别是胰岛素/IGF-1 样信号通路[10]。
此外,淫羊藿苷可能通过增强抗氧化酶(如 SOD)的活性,减少氧化损伤和炎症反应,这是衰老和许多慢性病的共同特征[17,18]。
淫羊藿苷在国内的批准现状
在国内,淫羊藿主要作为保健品和药品的原料使用,但尚未批准淫羊藿苷作为单一成分应用于保健食品原料和药物。但已批准的淫羊藿相关产品,如总黄酮提取物等中,含有淫羊藿苷成分。
哪些人群需慎用淫羊藿苷?
孕妇、哺乳期妇女及儿童:绝对禁用。
有出血倾向或正在服用抗凝/抗血小板药物者:可能增加出血风险。
心血管疾病患者(如高/低血压、心律失常、心力衰竭):可能影响心率和血压。
自身免疫性疾病患者:可能刺激免疫系统,导致病情活动。
激素敏感性疾病患者(如乳腺癌、子宫癌、前列腺癌、子宫内膜异位症):因其可能具有激素样效应。
肝、肾功能不全者:可能影响药物代谢和排泄,增加中毒风险。
手术前后患者:因其可能影响凝血和血压,需术前停药至少两周。
剂量信息
目前尚无统一的淫羊藿苷推荐剂量,一般根据不同的使用目的和产品形式而有所不同,如在一些保健食品中,每日推荐剂量可能在几十毫克到几百毫克不等,而在治疗某些疾病时,剂量会相对较高,但应在医生指导下使用。
参考资料:
[1]Ma, H. et al. The genus Epimedium: An ethnopharmacological and phytochemical review. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 134, 519–541 (2011).
[2]Li, C., Li, Q., Mei, Q. & Lu, T. Pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetic properties of icariin, the major bioactive component in Herba Epimedii. Life Sciences 126, 57–68 (2015).
[3]Cheng, T. et al. Comparative Pharmacokinetics Study of Icariin and icariside II in rats. Molecules 20, 21274–21286 (2015).
[4]Jin, J. et al. An outline for the pharmacological effect of icariin in the nervous system. European Journal of Pharmacology 842, 20–32 (2018).
[5]Schluesener, J. K. & Schluesener, H. Plant polyphenols in the treatment of age‐associated diseases: Revealing the pleiotropic effects of icariin by network analysis. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 58, 49–60 (2013).
[6]Cheng, S., Qiu, F., Wang, S. & He, J. HPLC analysis and pharmacokinetics of icariin in rats. Journal of Separation Science 30, 1307–1312 (2007).
[7]Chen, Y., Wang, J., Jia, X., Tan, X. & Hu, M. Role of intestinal hydrolase in the absorption of prenylated flavonoids present in Yinyanghuo. Molecules 16, 1336–1348 (2011).
[8]Yang, W. et al. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution profile of icariin propylene glycol-liposome intraperitoneal injection in mice. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 64, 190–198 (2011).
[9]Han, L.-Y., Wu, Y.-L., Zhu, C.-Y., Wu, C.-S. & Yang, C.-R. Improved Pharmacokinetics of Icariin (ICA) within Formulation of PEG-PLLA/PDLA-PNIPAM Polymeric Micelles. Pharmaceutics 11, 51 (2019).
[10]Cai, W.-J. et al. Icariin and its Derivative Icariside II Extend Healthspan via Insulin/IGF-1 Pathway in C. elegans. PLoS ONE 6, e28835 (2011).
[11]Liu, Y. et al. Icariin as an emerging candidate drug for anticancer treatment: Current status and perspective. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 157, 113991 (2022).
[12]Zhao, H., Mei, J., Huang, Q., Wang, H. & Xu, Z. Research progress of main components from Epimedii Folium (Yinyanghuo) in the treatment of male reproductive dysfunction and application & development status of Epimedii Folium. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 340, 119161 (2024).
[13]Zhang, G., Qin, L. & Shi, Y. Epimedium-Derived phytoestrogen flavonoids exert beneficial effect on preventing bone loss in late postmenopausal women: a 24-Month randomized, Double-Blind and Placebo-Controlled trial. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 22, 1072–1079 (2007).
[14]Lin, W.-L., Lin, P.-Y., Hung, Y.-C. & Hsueh, T.-P. Benefits of herbal Medicine on bone mineral density in Osteoporosis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine 48, 1749–1768 (2020).
[15]Yong, E.-L. et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to examine the safety, pharmacokinetics and effects of Epimedium prenylflavonoids, on bone specific alkaline phosphatase and the osteoclast adaptor protein TRAF6 in post-menopausal women. Phytomedicine 91, 153680 (2021).
[16]Zeng, J., Cheng, J., Zhu, L. & Tang, S. The effects of various nutritional supplements in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a network meta-analysis. BMC Pulmonary Medicine 25, (2025).
[17]Xia, J. et al. Icariin exhibits protective effects on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity via ROS-mediated oxidative stress injury in vivo and in vitro. Phytomedicine 104, 154331 (2022).
[18]Protective effects of icariin on neurons injured by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. PubMed https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16232349/ (2005).
