总结卡片
SUMMARY
24
Changshou.com
α-硫辛酸
(Alpha-lipoic acid)
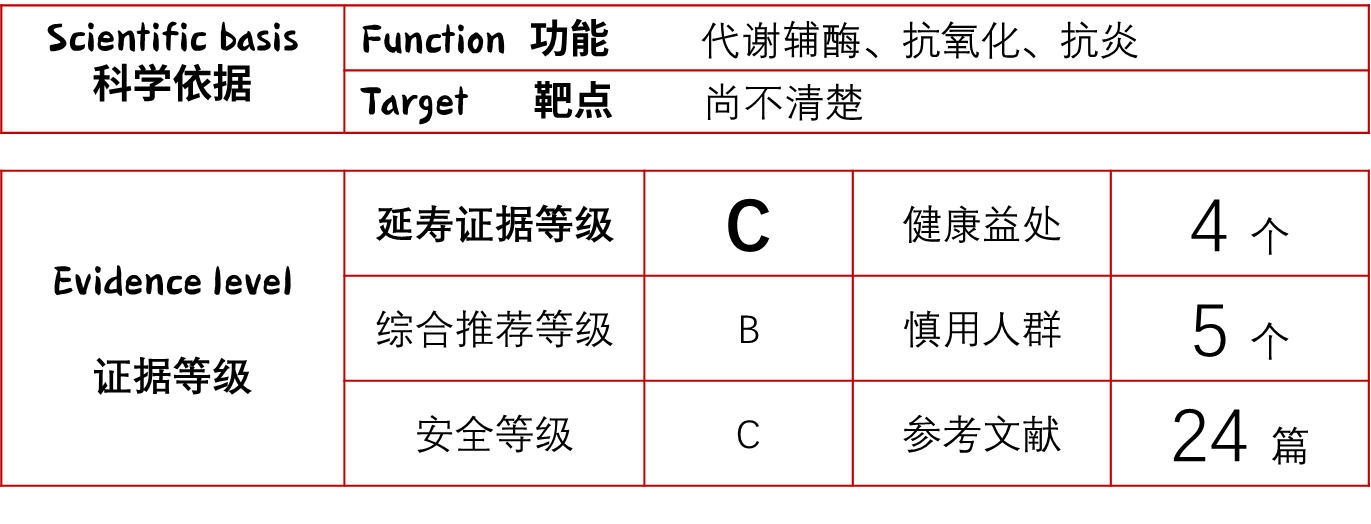
α-硫辛酸(Alpha-lipoic acid)是一种强大的含硫抗氧化剂,被称为“抗氧化剂中的抗氧化剂”。它还作为辅酶参与线粒体的能量代谢,兼有抗炎、神经保护等功能[1]。与传统认知不同,α-硫辛酸在改善老年早衰小鼠的记忆力的同时,却缩短了小鼠的寿命[2]。
什么是 α-硫辛酸?
α-硫辛酸(Alpha-lipoic acid , ALA) 也称 6,8-二硫辛酸、二硫辛酸,简称硫辛酸,是一种含硫的八碳脂酸,具有独特的双硫键结构,兼具水溶性和脂溶性,可广泛分布于细胞内外,在生物体内发挥多种生理功能[3,4]。
α-硫辛酸作为强大的抗氧化剂,可以清除活性氧(ROS),还参与线粒体的能量代谢,改善线粒体功能[5]。在临床上,硫辛酸常被用于治疗由糖尿病周围神经病变导致的感觉异常[6,8]。
硫辛酸有两种对映体,分别为 R-型和 S-型,自然界中以R-型存在,也是生物活性更强的形式[7]。人体可以合成硫辛酸。目前,尚未发现人类有硫辛酸的缺乏症。
α-硫辛酸:延寿证据等级 C,为什么?
α-硫辛酸可以延长果蝇和线虫的寿命[9-11]。但对于小鼠来说,结果没那么乐观[2]。
2012 年的一项研究对早衰小鼠(SAMP8)从 11 个月大开始施用 α-硫辛酸,直至死亡。发现 α-硫辛酸可以改善小鼠的记忆力并逆转氧化应激,但是寿命缩短了14周[2]。
另一项更早的大鼠实验则发现,乙酰左旋肉碱和R-硫辛酸联合喂养,可以改善细胞的新陈代谢并降低氧化应激[12]。
根据长寿之家Changshou.com制定的《长寿成分评级标准(2025版)》,硫辛酸的延寿证据等级为C。
补充 α-硫辛酸有什么好处?
α-硫辛酸对人类健康的多方面益处已在大量临床试验中得到验证。虽然没有直接以“延长寿命”为终点的长期人类试验,但其对多种衰老相关疾病的改善作用,间接支持了其促进健康长寿的潜力。
神经保护作用:一项为期 2 年的随机双盲对照试验,招募了 51 名年龄在 40-70 之间的继发性多发性硬化症(MS)患者,研究发现, 患者每日口服 1200 毫克的硫辛酸,2 年后脑容量的减少幅度显著小于预期[13]。
治疗 2 型糖尿病并发症:一项纳入 16 篇研究的荟萃分析结果显示,α-硫辛酸通过口服和静脉两种给药途径,都有降低糖尿病性多发性神经病疼痛的功效[14]。
另一项纳入 10 项随机对照临床试验,总样本量为 1242 的荟萃分析结果显示,每天口服 α-硫辛酸 600- 1800 毫克,可通过减少氧化应激和改善微循环,能显著改善糖尿病感觉运动周围神经病变(DSPN)患者的症状[15]。
男性生殖健康:一项三盲随机对照试验结果显示,每天 600 毫克 α-硫辛酸,持续 80 天,可以改善精索静脉曲张切除术后不育男性的精子活力[16]。
另一项纳入 250 名年龄在 25-40 岁之间不育男性的荟萃分析结果显示,α-硫辛酸可以显著改善精子参数,提高精子功能[17]。
还有一项随机对照试验表明,α-硫辛酸、葡萄和银杏叶的组合可以治疗男性勃起功能障碍[18]。
改善血管内皮功能:一项纳入 300 名受试者的荟萃分析评估了 α-硫辛酸对内皮功能的影响,发现补充 α-硫辛酸似乎可以改善血管内皮功能,预防心血管疾病[19]。
吃了 α-硫辛酸身体会有何变化?
精力提升:由于线粒体功能增强,能量产生更高效。
头脑更清晰:神经保护作用可能带来认知功能的轻微改善。
血糖更稳定:特别是对于有胰岛素抵抗的人,饭后困倦感可能减轻。
神经病变症状减轻:对于相关患者,疼痛和麻木感得到缓解。
α-硫辛酸的安全性与副作用
α-硫辛酸通常耐受性良好。有些人可能会出现轻微的胃肠道副作用,例如恶心、呕吐和胃灼热。还有一些关于局部使用皮肤刺激的报道,包括接触性皮炎和皮疹、瘙痒等[20]。
α-硫辛酸是如何发挥功能的?
丙酮酸脱氢酶复合物是一种参与能量产生的关键酶,α-硫辛酸通过作为丙酮酸脱氢酶复合物的辅助因子参与线粒体中的细胞呼吸,减少线粒体在能量生产过程中产生的自身活性氧自由基(ROS)[13]。
α-硫辛酸可以激活 Nrf2(核因子E2相关因子2)信号通路。Nrf2 是细胞抗氧化反应的“总开关”,被激活后会进入细胞核,启动上百种保护性基因的表达,包括 II 相解毒酶和内源性抗氧化酶(如超氧化物歧化酶 SOD、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶),从而系统性地增强细胞的防御能力[21-23]。
α-硫辛酸还能激活 AMPK(AMP活化蛋白激酶),这是一种细胞的能量感受器。AMPK 的激活可以促进葡萄糖摄取和脂肪酸氧化,类似于运动的效果,从而改善胰岛素信号传导和代谢健康[24]。
α-硫辛酸在国内批准现状
在中国,α-硫辛酸被国家药品监督管理局(NMPA)批准为药品,主要用于治疗糖尿病周围神经病变引起的感觉异常。
目前,α-硫辛酸在国内已被列入化妆原料目录,但尚未获得保健食品、食品添加剂或新食品原料许可。在日本,α-硫辛酸被批准作为膳食补充剂原料使用。
哪些人群需慎用α-硫辛酸?
糖尿病患者:硫辛酸本身能降血糖,与糖尿病药物(如胰岛素或口服降糖药)合用可能增加低血糖风险。如需使用,必须在医生指导下密切监测血糖并调整药物剂量。
甲状腺功能减退患者:有少量研究表明高剂量硫辛酸可能干扰甲状腺激素的功能,甲减患者应谨慎使用并监测甲状腺水平。
孕妇及哺乳期妇女:由于缺乏足够的安全研究数据,建议此类人群避免服用硫辛酸补充剂。
服用抗凝药物的人群:α-硫辛酸可能具有抗血小板特性,理论上可以增强抗血小板药物的作用并增加出血风险。
缺乏生物素的人群:生物素和 α-硫辛酸使用相同的转运蛋白被人体吸收,所以同时服用它们可能会竞争吸收。
剂量信息
α-硫辛酸的标准剂量在 300-600 毫克之间,不同的异构体之间没有区别。
参考资料:
[1]Superti, F. & Russo, R. Alpha-Lipoic acid: biological mechanisms and health benefits. Antioxidants 13, 1228 (2024).
[2]Morley, J., Price, T., Banks, W., Ercal, N. & Farr, S. P2‐439: Alpha‐lipoic acid affects memory and lifespan in SAMP8 mice. Alzheimer S & Dementia 8, (2012).
[3]Reed, L.J.; Debusk, B.G.; Gunsalus, I.C.; Hornberger, C.S., Jr. Crystalline alpha-lipoic acid; a catalytic agent associated with pyruvate dehydrogenase. Science 1951, 114, 93–94.
[4]Bustamante, J.; Lodge, J.K.; Marcocci, L.; Tritschler, H.J.; Packer, L.; Rihn, B.H. Alpha-lipoic acid in liver metabolism and disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 24, 1023–1039.
[5]Dörsam, B. & Fahrer, J. The disulfide compound α-lipoic acid and its derivatives: A novel class of anticancer agents targeting mitochondria. Cancer Letters 371, 12–19 (2015).
[6]Dilworth, L. et al. Diabetes and the associated complications: The role of antioxidants in diabetes therapy and care. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 181, 117641 (2024).
[7]Watson, P.R.; Stollmaier, J.G.; Christianson, D.W. Crystal structure of histone deacetylase 6 complexed with (R)-lipoic acid, an essential cofactor in central carbon metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105228.
[8]Ziegler, D. Pathogenetic treatments for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 206, 110764 (2023).
[9]Du, G. et al. Lipoic acid rejuvenates aged intestinal stem cells by preventing age‐associated endosome reduction. EMBO Reports 21, (2020).
[10]Benedetti, M. G. et al. Compounds that confer thermal stress resistance and extended lifespan. Experimental Gerontology 43, 882–891 (2008).
[11]Brown, M., Evans, J. & Luo, Y. Beneficial effects of natural antioxidants EGCG and α-lipoic acid on life span and age-dependent behavioral declines in Caenorhabditis elegans. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 85, 620–628 (2006).
[12]Hagen, T. M. et al. Feeding acetyl- l -carnitine and lipoic acid to old rats significantly improves metabolic function while decreasing oxidative stress. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 99, 1870–1875 (2002).
[13]Spain, R. et al. Lipoic acid in secondary progressive MS. Neurology Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation 4, (2017).
[14]Cassanego, G., Rodrigues, P., De Freitas Bauermann, L. & Trevisan, G. Evaluation of the analgesic effect of ɑ-lipoic acid in treating pain disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacological Research 177, 106075 (2022).
[15]Hsieh, R.-Y., Huang, I.-C., Chen, C. & Sung, J.-Y. Effects of Oral Alpha-Lipoic Acid Treatment on Diabetic Polyneuropathy: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Nutrients 15, 3634 (2023).
[16]Abbasi, B., Molavi, N., Tavalaee, M., Abbasi, H. & Nasr-Esfahani, M. H. Alpha-lipoic acid improves sperm motility in infertile men after varicocelectomy: a triple-blind randomized controlled trial. Reproductive BioMedicine Online 41, 1084–1091 (2020).
[17]Pires, I. Z. et al. Efficacy of alpha lipoic acid supplementation in sperm Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. PubMed 51, (2025).
[18]Derosa, G., D’Angelo, A., Preti, P. S. & Maffioli, P. Evaluation of the Effect on Sexual Performance of a Nutraceutical Combination Containing Alpha Lipoic Acid, Vitis vinifera L. and Ginkgo biloba, Compared to Placebo, Avanafil or a Combination of Nutraceutical Plus Avanafil in Males With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Erectile Dysfunction. Frontiers in Endocrinology 13, (2022).
[19]Jalilpiran, Y. et al. The effect of Alpha‐lipoic acid supplementation on endothelial function: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Phytotherapy Research 35, 2386–2395 (2020).
[20]Velasco‐Amador, J. P., Prados‐Carmona, Á. & Navarro‐Triviño, F. J. Contact urticaria syndrome caused by alpha‐lipoic acid in a master formula for vulvar lichen sclerosus. Contact Dermatitis 89, 136–137 (2023).
[21]Shay, K. P., Moreau, R. F., Smith, E. J., Smith, A. R. & Hagen, T. M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects 1790, 1149–1160 (2009).
[22]Flier, J., Van Muiswinkel, F. L., Jongenelen, C. A. M. & Drukarch, B. The Neuroprotective Antioxidant α-lipoic Acid Induces Detoxication Enzymes in Cultured Astroglial Cells. Free Radical Research 36, 695–699 (2002).
[23]Shay, K. P., Michels, A. J., Li, W., Kong, A.-N. T. & Hagen, T. M. Cap-independent Nrf2 translation is part of a lipoic acid-stimulated detoxification stress response. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 1823, 1102–1109 (2012).
[24]Lee, W. J. et al. α-Lipoic acid increases insulin sensitivity by activating AMPK in skeletal muscle. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 332, 885–891 (2005).
